How to Calculate COGS for Your Amazon Business
Updated April 21, 2023

In order to be successful as an Amazon seller, you need to know your cost of goods sold (COGS). This calculation is essential for understanding your business profitability and determining your markup.
This article will cover two methods for calculating COGS for your Amazon business, as well as what costs are and are not included in this metric.
Calculate by Hand Using the COGS Formula
The formula for calculating COGS is as follows:
cost of goods sold = (beginning inventory + purchases) - ending inventory
This equation calculates the total cost of all the goods sold over a specific period.
As an example, let's say during the commencement of the financial year, to stock your online store, you've purchased $5,000 worth of t-shirts. As the year pans out, you purchase an additional $7,000 worth of t-shirts to restock and keep up with projected demand. By the end of the year, you've sold all but $2,000 worth of stock.
If this was the case, the COGS for your Amazon store would look like this:
$5,000 + $7,000 - $2,000 = $10,000.
Automatically Calculate COGS
BeProfit provides a straightforward platform for tracking key metrics and calculating COGS.
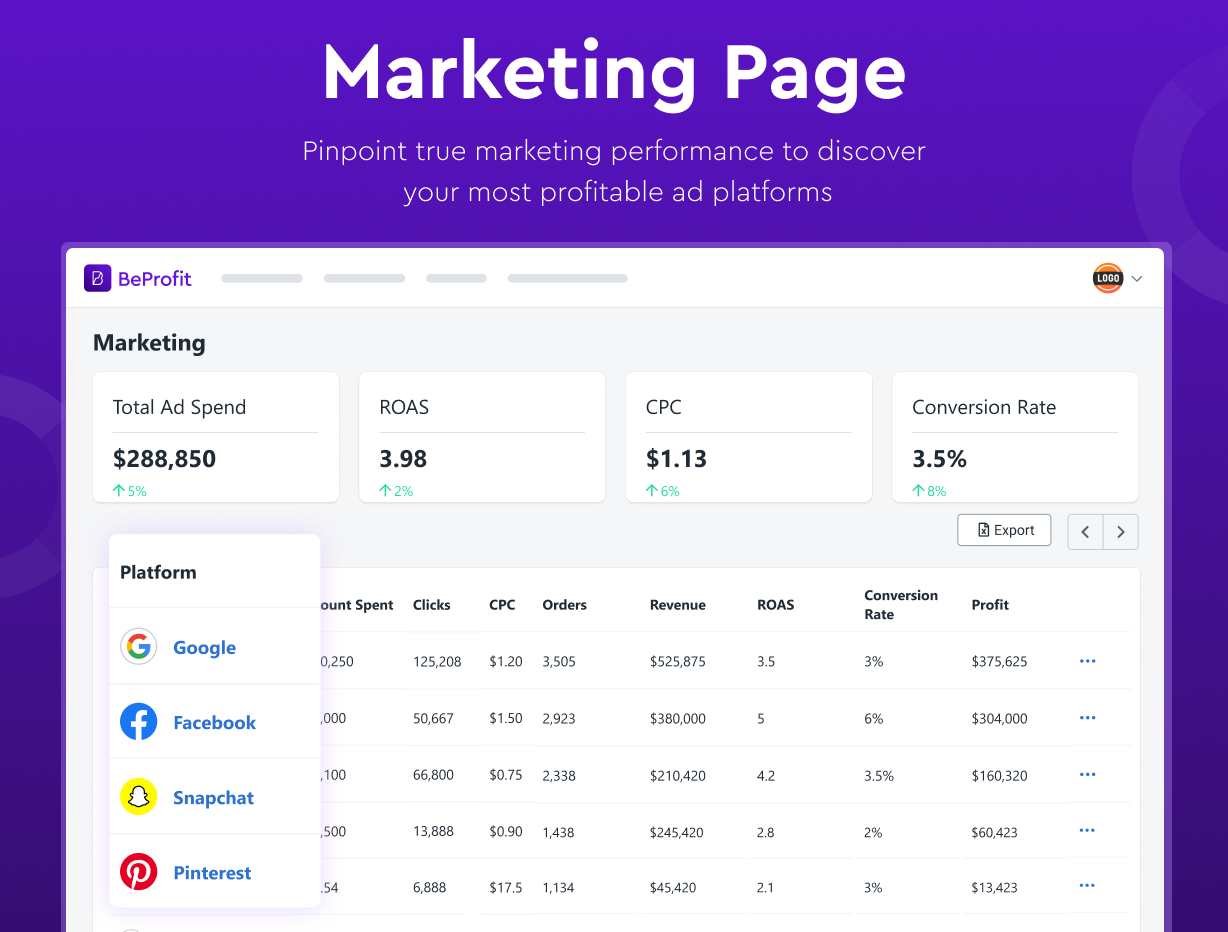
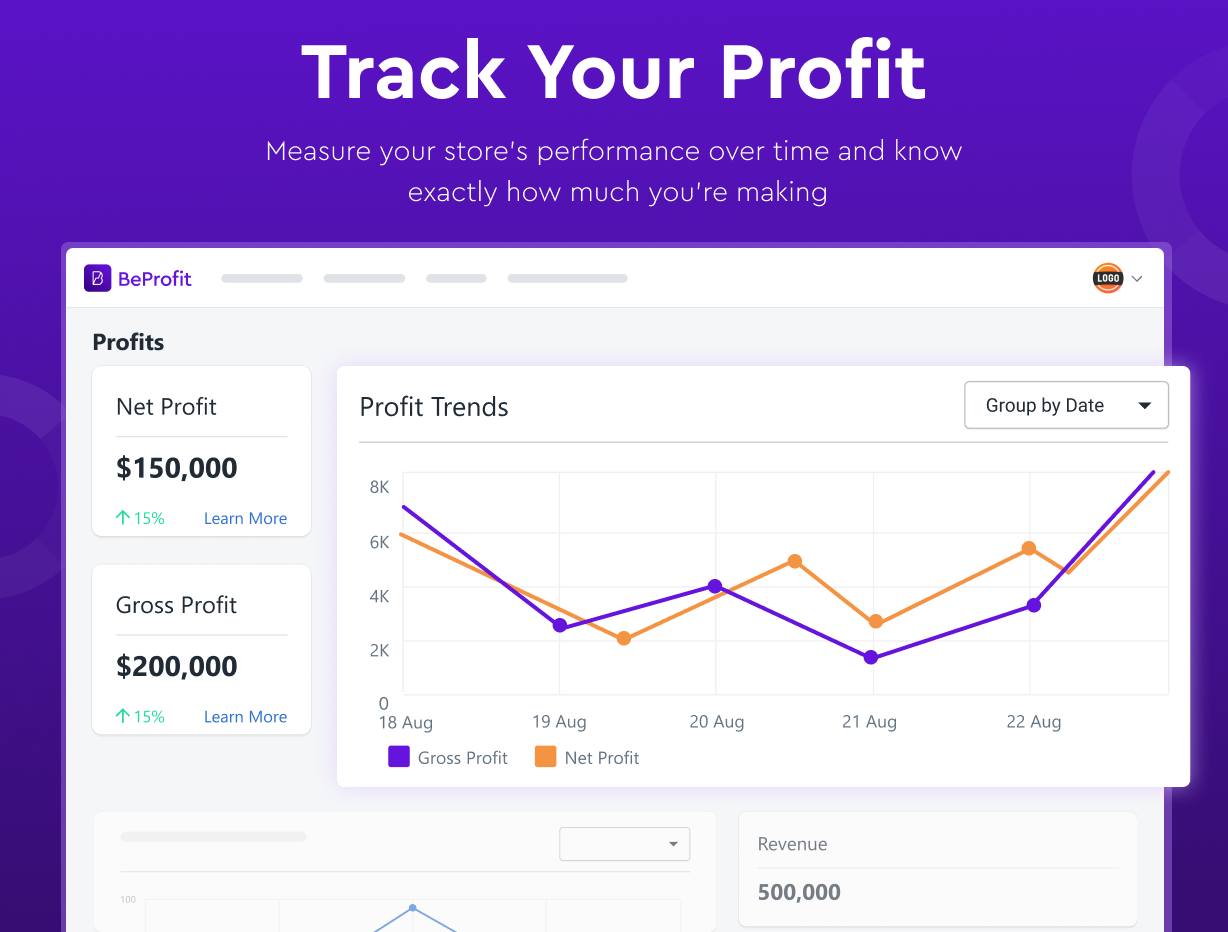
- Get up-to-date reports on e-commerce COGS, shipping costs, processing fees, and more.
- Use advanced techniques like cohort analysis to gain in-depth knowledge of customer lifetime value (LTV) and marketing performance.
- Connect all your stores and view business performance as a whole. Set up simple, once-and-done integrations to automatically pull in data on advertising and shipping.
- Share your workspace with your team and work together in real time from any device.
» Find out how you can calculate your Amazon ROAS
What Is and Isn't Included in E-Commerce COGS?
In order to calculate sales metrics such as gross margin and gross profit, the cost of goods sold is subtracted from a company's revenue, signifying that the higher the cost of goods sold, the lower the revenue margins.
However, certain business expenses will not be accounted for in your COGS. Knowing what to include and what to exclude can lead to more precise calculations.
Included Expenses
There are several expenses included in COGS, such as:
- Procurement costs Procurement costs are the expenses associated with the purchase of goods and services. This includes the cost of the goods or services themselves, as well as any associated transportation, administrative, or inspection costs.
- Production expenses Production expenses are the costs of producing a good or service. These costs can include materials, labor, and overhead.
- Packaging, handling fees, and freight costs Packaging, handling, and freight costs are the costs associated with the packaging and shipment of a product. This includes the materials used for packaging, as well as the labor involved in packaging and transporting a product.
- Inventory storage expenses Inventory storage expenses represent the costs associated with storing a company's inventory. These costs can include the cost of the physical space used to store the inventory, as well as the cost of any insurance or security measures needed to protect the inventory.
- Listing fees Online product listing fees are a way for companies to list their products on online marketplaces like Amazon.
- Taxes They are represented by any applicable taxes that are payable to government bodies as a result of running an online business.
» Learn how to reduce your COGS using three insights
Excluded Expenses
The following expenses are not included in COGS:
- Rent Rent is not included in COGS because it is not a direct expense associated with the production of a good or service.
- Utilities Utilities are not included in COGS because they are not the direct costs of producing a good or service. Instead, they are indirect costs that are necessary for producing a good or service but are not directly related to the production process.
- Insurance The reason that insurance is not included in COGS is that it is a fixed expense. COGS are intended to reflect the costs of the goods that are sold, and insurance does not vary with the amount of product that is sold.
- Sales and marketing Sales and marketing activities are necessary for a company to generate revenue, but they are not directly related to the production of goods.
Do the Math
Calculating COGS is an important step in understanding the profitability of your Amazon business. By using the methods described in this article, you can accurately track your costs and make informed decisions about how to grow your online business.
» Boost your Amazon store's profits by using effective e-commerce ads








