Incremental Cost vs Marginal Cost: 5 Ways They Affect Your Business
Updated April 25, 2023

Statista forecasts that e-commerce sales are expected to reach around $8.1 trillion by 2026. To gain efficient revenue and make informed decisions, you need to understand the cost of producing goods and services. Two related concepts that are used in this context are incremental and marginal costs. While these terms are often used interchangeably, they have distinct meanings that are important to distinguish between.
» Learn about effective cost leadership strategies with examples
Difference Between Incremental and Marginal Cost
Incremental Cost
Incremental cost refers to the cost of producing an additional unit of output, taking into account all costs that vary with the level of production, including fixed costs.
Some costs may include:
- Power usage
- New production line implementation
- Upgraded equipment
The costs may differ depending on the step in production. To work out the incremental cost per additional unit, you can use the following formula:
Incremental Cost = Variable Costs / Units Produced
Marginal Cost
Marginal cost, on the other hand, refers to the cost of producing an additional unit of output, considering only the variable cost associated with that unit.
These variable costs may include:
- Labor
- Materials
To calculate the marginal cost per new unit, you can use the following formula:
Marginal Cost =
(Future Costs - Current Costs) / (Future No. of Units - Current No. of Units)
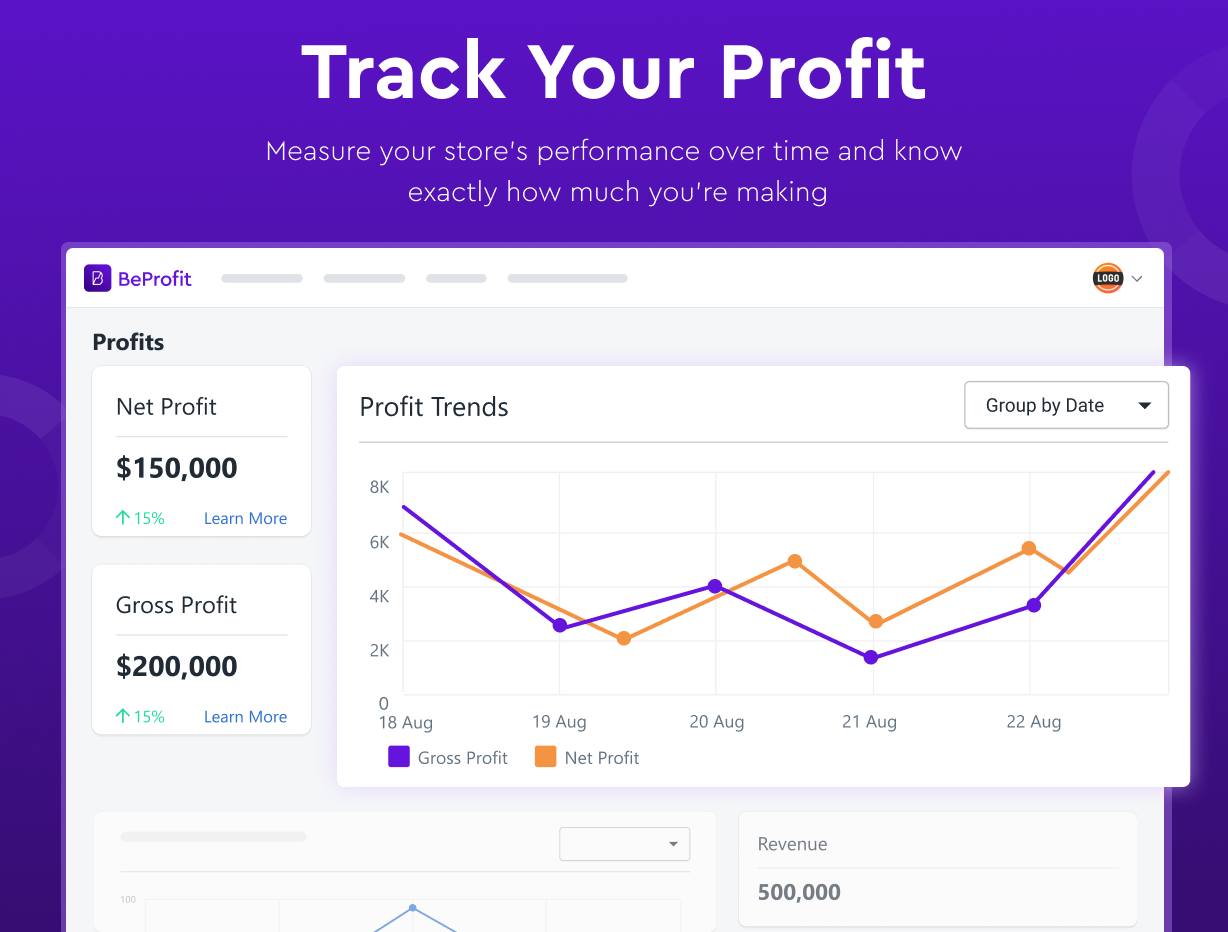
Track Your Costs With Ease
Monitor your store's—or multiple stores'—profits, revenue, and expenses from one dashboard.
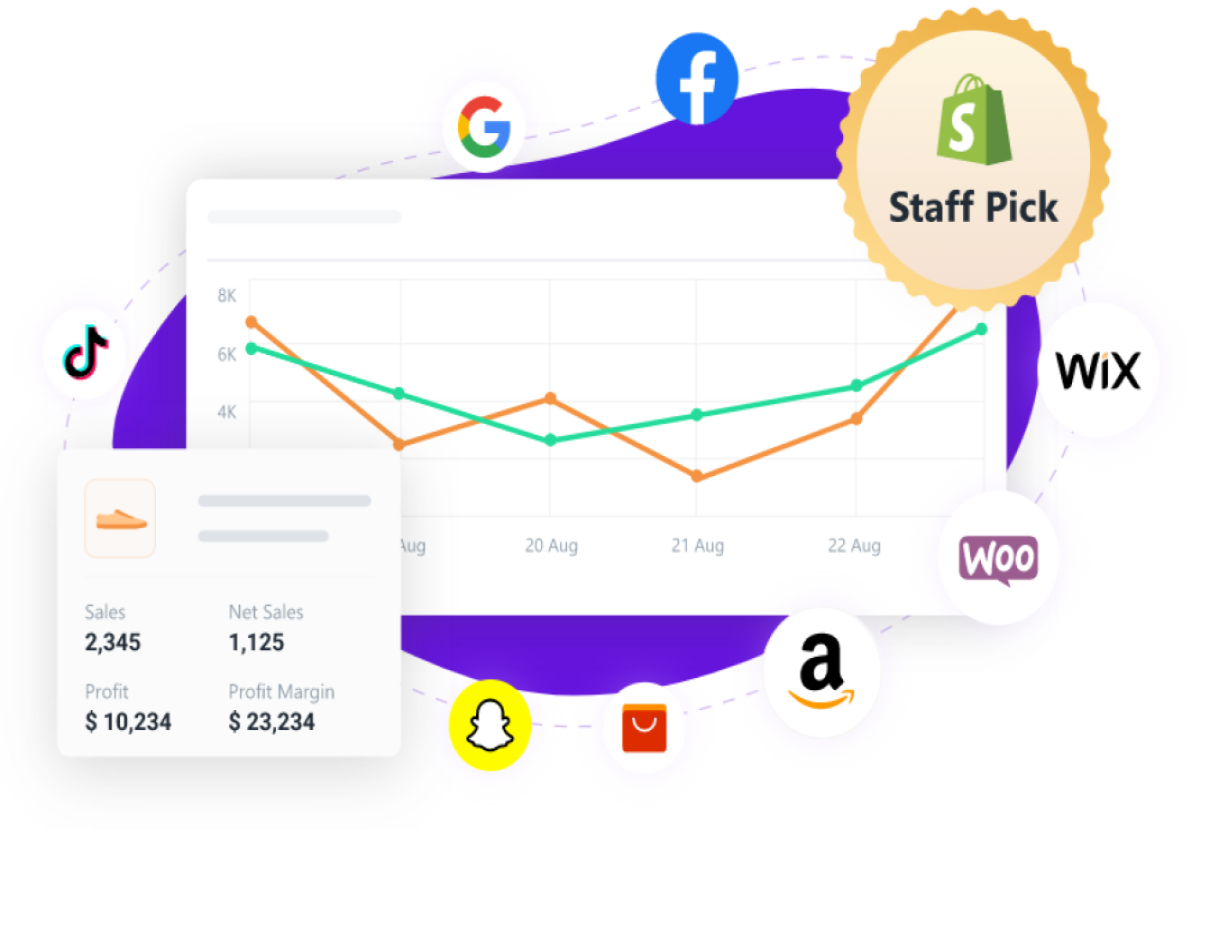
- Effortlessly visualize complex data with charts and graphs.
- Get up-to-date data reports on COGS and processing and shipping fees.
- Access your data from anywhere using a desktop or mobile device.
With BeProfit you can monitor and track your business's revenue metrics and costs per order in real time.
How Do These Costs Affect Your Business?
These costs can have negative and positive impacts on a business's strategies and revenue, depending on the accuracy of calculations. Some areas of impact include:
Profitability
In manufacturing and retail businesses, knowing the marginal cost of each unit produced can help determine the optimal production level and pricing strategies that can increase your profit margins. Additionally, knowing the cost associated with each production unit helps businesses allocate resources effectively to different products or services.
Product Volume
If the incremental cost of producing additional units is higher than the selling price, then it is not profitable to produce them. And if the marginal cost of producing an additional unit is lower than the selling price, producing more units may increase profitability.
Therefore, businesses need to carefully consider both costs when deciding on the volume of production.
» Want to organize product volume? See the best Wix inventory management apps
Product Pricing
If the incremental cost of producing additional units exceeds the product selling price, you aren't likely to gain a profit. And if the marginal cost of producing an additional unit is lower than the product selling price, then a business may be able to offer lower prices and still maintain product profitability.
Volume discounts may work, for instance, if marginal costs are low, whereas higher prices may be necessary if incremental costs are high.
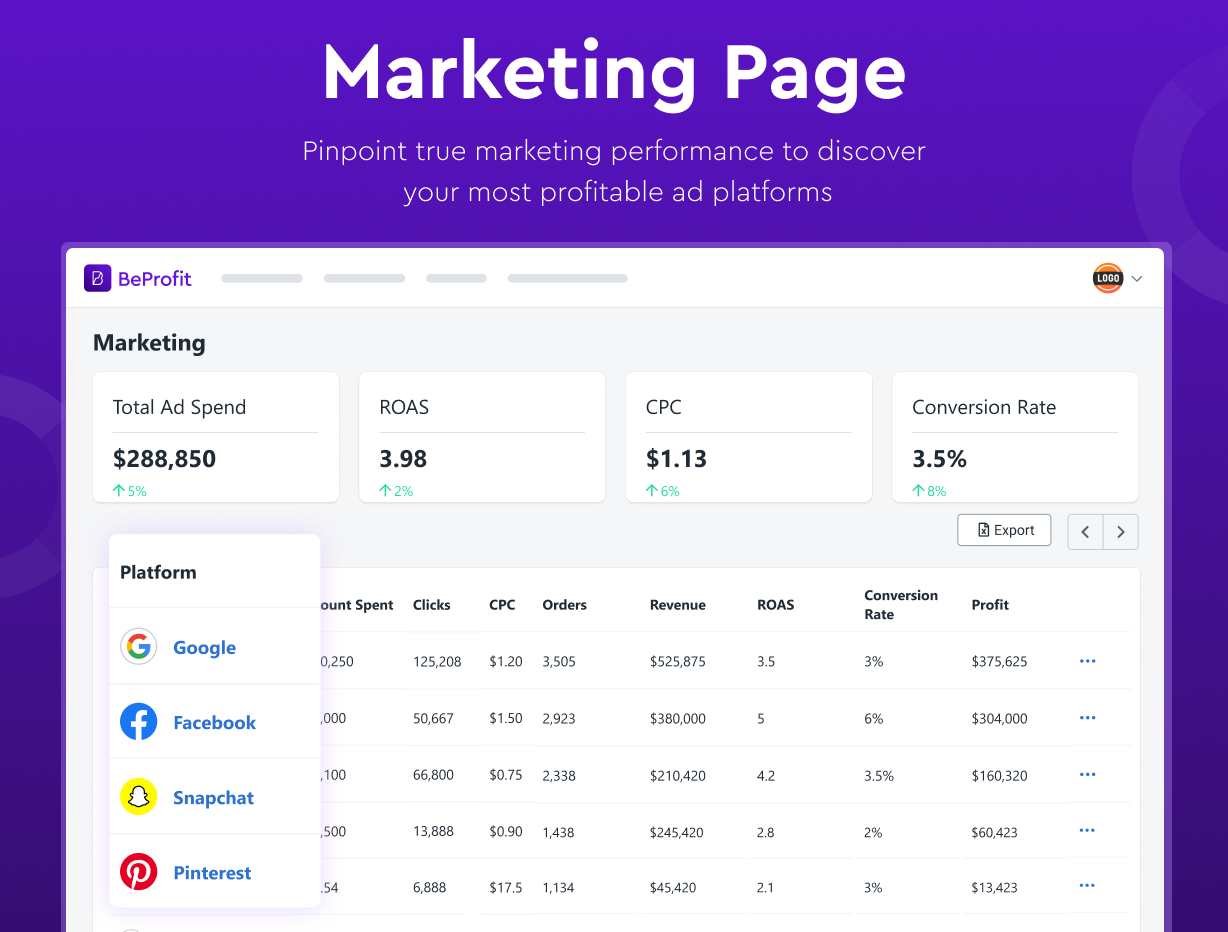
Marketing Reach
Marketing costs may include:
- Specialized marketers
- Investments into new software or platforms
If the incremental cost of reaching an additional customer exceeds the expected revenue generated by that customer, then you may need to lower your cost per acquisition (CPA) and rework the strategy. Conversely, if the marginal cost of reaching one additional customer is lower than the revenue generated by that customer, then it may be a profitable marketing strategy.
Production Changes
Incremental and marginal costs both play a critical role in determining production and how it changes due to the effects it has on the business. Some changes may include:
- Altering the steps of the production line
- Increasing production numbers
- Outsourcing
If the incremental cost of the changed method exceeds the marginal revenue generated by the units it can turn out, then it may not be economically viable. And if the marginal revenue generated by producing additional units, more example, exceeds the marginal cost, then increasing production may be profitable.
» Got excessive costs? Check out these insights on how to reduce your COGS
Keep Costs in Mind and Run Your Business Confidently
Incremental and marginal costs are fundamental business concepts that help you make confident and informed decisions about production, pricing, and marketing. A level of confidence plays a major role in growing your business and sustaining it long-term.
By tracking the efficiency of these e-commerce expenses, you can make strategic adjustments in a timely manner. With BeProfit's platform, you can monitor expense metrics in real time all from one dashboard, making it easier to implement changes that can maximize your bottom line.








